It is thus wise to divide an electric power system into different protective zones, which is why power protection is classified as generator protection, transformer protection, transmission line protection, motor protection, bus-bar protection, etc.
ABOUT PROTECTION ZONES:
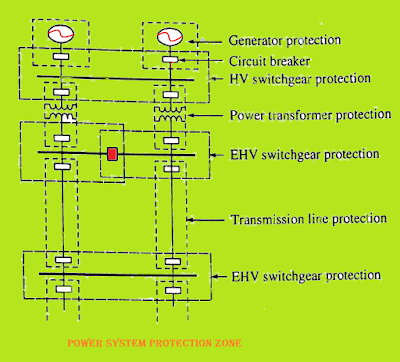
A power system network consists of different types of equipment and associated elements like generators, transformers, primary transmission, primary distribution, secondary distribution,sub-stations, etc. Protective schemes depend on the type and nature of the equipment to be protected. It is thus wise to divide an electric power system into different protective zones, which is why power protection is classified as generator protection, transformer protection, transmission line protection, motor protection, bus-bar protection, etc. The planning for protective zones is done in such a way that the zones cover the entire power network collectively. Overlapping of the zones is allowed in order to avoid the unprotected areas. If an area remains unprotected , it means that any fault occurring in that area would not be cleared at all and such an area is called blind spot. For a fault occurring in the area of two overlapped zones, the circuit breakers in both the directions will isolate the faulted area.
The protection zones of a typical power system are like this picture in below-
 |
| Zone Protection |
Thus, overlapping will trip all the circuit breakers in both the zones even through a fault may have occurred on one side.



Post a Comment
Post a Comment